What Do Kinkajous Eat
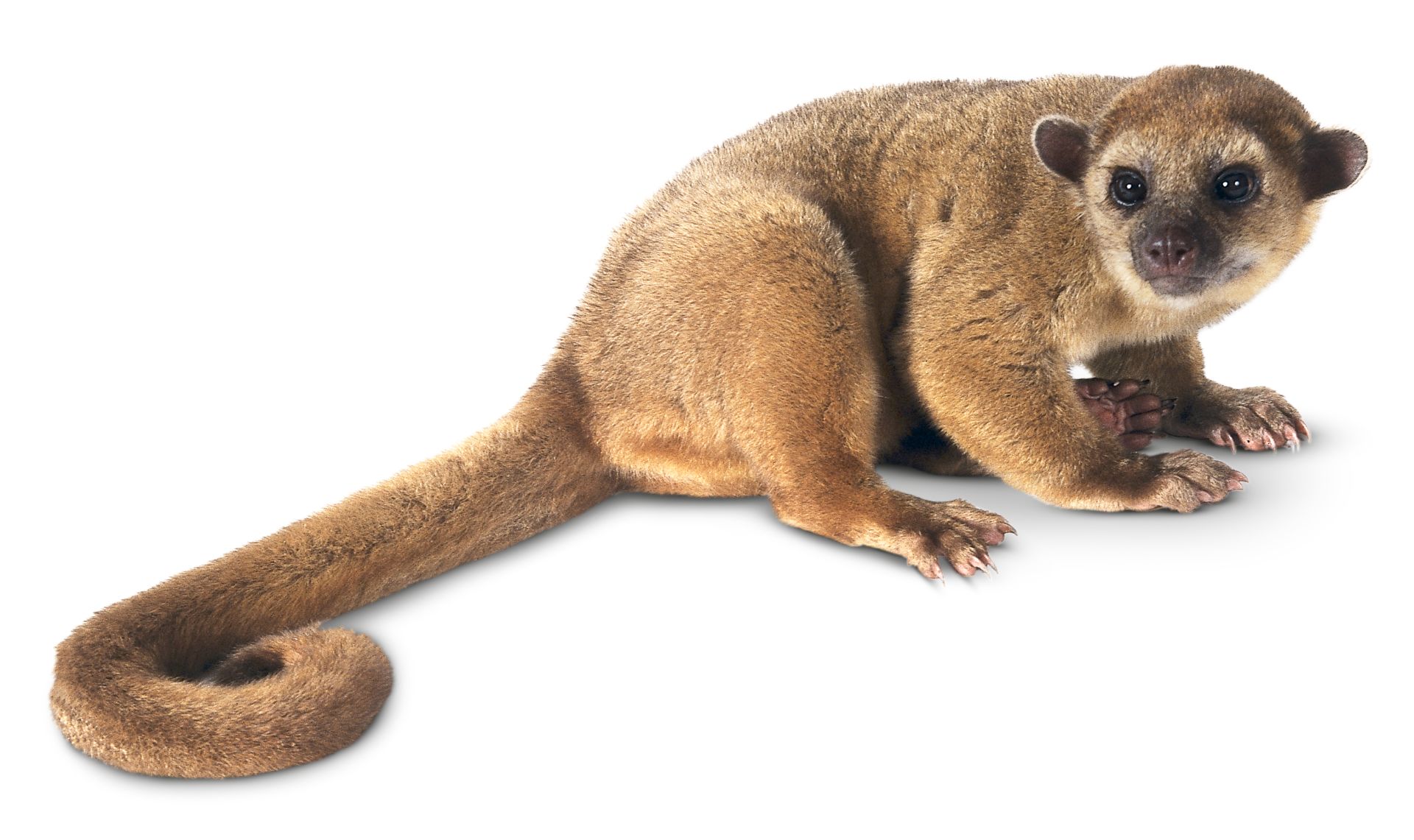
Kinkajous are small, nocturnal mammals that live in the rainforests of Central and South America. They are also known as “honey bears” because they love to eat honey! Kinkajous have long, prehensile tails that they use to grip branches as they climb through the trees.
They have furry bodies and big eyes, which help them see at night. Kinkajous mostly eat fruit, but they will also eat insects, small reptiles, and even baby birds!
What Do the Kinkajous Eat in a Day?
Kinkajous are small mammals that live in Central and South America. They are closely related to raccoons and have a similar diet. Kinkajous typically eat fruit, but they will also eat insects, small reptiles, and birds.
What Fruit Do Kinkajous Eat
Kinkajous are small, nocturnal mammals that are native to the rainforests of Central and South America. These furry creatures are closely related to raccoons and have a long, prehensile tail that they use to climb trees in search of food. Kinkajous are omnivorous and their diet consists of fruits, flowers, leaves, insects, and small vertebrates.
Fruit is an important part of the kinkajou’s diet and they will often spend hours foraging through the forest canopy in search of ripe fruit to eat. Some of the most common fruits that kinkajous eat include bananas, figs, papayas, and grapes. While they will eat just about any type of fruit they can find, these four fruits make up a large part of their diet.
Kinkajous play an important role in the rainforest ecosystem as they help to disperse seeds from the fruits they eat. By eating fruit and then defecating elsewhere, kinkajous help to spread plant life throughout the forest.
How Many Kinkajous are Left in the World
Kinkajous are small, nocturnal mammals that are native to the rainforests of Central and South America. They are also known as “honey bears” due to their love of sweet fruits. Kinkajous have long, prehensile tails and furry bodies with golden-brown fur.
They are proficient climbers and can often be seen suspended upside-down from branches.
Sadly, kinkajous are now considered to be endangered due to habitat loss and hunting pressure. It is estimated that there may be as few as 10,000 kinkajous remaining in the wild.
This is a drastic decline from just a few decades ago when they were thought to number in the hundreds of thousands.
If we want to save kinkajous from extinction, it is imperative that we take action to protect their remaining forest habitats. We must also work to reduce the demand for kinkajou products such as skins and meat.
Only by taking these steps will we be able to ensure that these fascinating creatures remain a part of our world for generations to come.
Do Kinkajous Bite
Do kinkajous bite? The answer may surprise you.
Kinkajous are small, nocturnal mammals native to the rainforests of Central and South America.
They’re closely related to raccoons and have long, prehensile tails that they use to climb trees. Kinkajous are also sometimes called “honey bears” because they love to eat honeycombs – hence their other nickname, “the honey bear.”
Despite their cuddly appearance, kinkajous can be rather aggressive animals.
They have sharp claws and teeth, which they’re not afraid to use if they feel threatened. While kinkajous aren’t known to attack humans, there have been reports of them biting people who’ve tried to handle them. So if you ever encounter a kinkajou in the wild, it’s best to admire it from a distance!
Where Do Kinkajous Live
Kinkajous are small, tree-dwelling mammals that are native to Central and South America. They are nocturnal animals, meaning they are most active at night. Kinkajous typically live in rainforests, but can also be found in dryer forest habitats as well.
Kinkajous have long tails and furry bodies, and their diet consists mostly of fruit.
Kinkajous are very shy animals and are not often seen by humans. If you’re lucky enough to spot one, it’s likely you’ll see them high up in a tree, eating fruit or leaves.
Kinkajous rarely come down to the ground, so they’re not often seen by people walking through the forest.
Are Kinkajous Dangerous
Kinkajous are small, furry animals that look like a cross between a monkey and a teddy bear. They’re native to Central and South America, and while they might look cute, they can actually be quite dangerous.
For one thing, kinkajous have razor-sharp claws that they use for climbing trees.
They also have long, sharp teeth that they use for biting. If a kinkajou were to bite you, it would be very painful and could even cause infection.
Another danger of kinkajous is that they carry a lot of diseases.
Some of these diseases, like rabies, can be deadly. So, if you’re ever bitten by a kinkajou, make sure to get medical help right away.
Lastly, kinkajous are wild animals and should not be kept as pets.
They can be very aggressive and may bite or scratch if they feel threatened. If you’re looking for a cuddly pet, stick with a teddy bear!
Do Kinkajous Make Good Pets
Kinkajous are small, nocturnal mammals that are native to the rainforests of Central and South America. These interesting animals are also known as “honey bears” due to their love of sweet foods. While they are often kept as exotic pets, kinkajous can be difficult to care for and may not be the best choice for everyone.
If you’re considering a kinkajou as a pet, there are a few things you should know first. For starters, kinkajous require a lot of care and attention. They are active animals that need plenty of space to roam and explore.
Kinkajous also have special dietary needs and should only eat fruit, vegetables, and insects – no processed or sugary foods.
Another important consideration is that kinkajous can be nippy creatures. They have sharp teeth and claws that can cause serious injury if they feel threatened or scared.
As such, kinkajous may not be suitable for homes with small children or other pets.
Before making the decision to adopt a kinkajou, do your research to make sure you understand what’s involved in caring for one of these unique animals.
What Does a Kinkajou Do
A kinkajou is a nocturnal rainforest mammal of the family Procyonidae related to raccoons and olingos. It is also known as the “nightwalker”, ” night bear” or ” rainforest bumblebee”. The kinkajou is the only member of the genus Potos and its name comes from the Carib word for “honey bear”.
Kinkajous are about the size of a house cat, with a long tail and furry body. They have large eyes, rounded ears, and short legs. Their fur is usually reddish-brown or yellowish-brown, but can be nearly black.
Kinkajous are excellent climbers and often hang upside down from branches.
Kinkajous eat fruit, leaves, honey, insects, small mammals, and birds. They play an important role in dispersing seeds throughout the rainforest.
Kinkajous are native to Central and South America but can now be found in zoos around the world.

Credit: www.kinkatopia.org
What Do You Feed a Kinkajou?
A kinkajou is a type of mammal that is native to the rainforests of Central and South America. They are also known as “honey bears” due to their love of sweet fruits. In the wild, kinkajous eat a diet that consists mostly of fruit, but they will also consume leaves, insects, and small vertebrates.
In captivity, kinkajous can be fed a diet that includes fruits, vegetables, cooked meats, and commercially-prepared monkey chow. It is important to provide them with a variety of foods to meet their nutritional needs. Kinkajous should also have access to fresh water at all times.
What Can Kinkajous Not Eat?
There are a few things that kinkajous cannot eat, such as:
-Fruits with pits or seeds: Kinkajous have delicate digestive systems and can’t handle the pits or seeds from fruits like apricots, cherries, plums, etc.
-Tough vegetables: Kinkajous also can’t eat tough vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, or kale.
These veggies are hard to digest and can cause stomach issues for kinkajous.
-Spicy food: Like many people, kinkajous can’t handle spicy food very well. So it’s best to avoid giving them anything with a lot of spice or heat.
Overall, kinkajous are relatively easy to please when it comes to their diet. As long as you avoid the foods listed above, they should be happy and healthy!
What Fruits Do Kinkajous Eat?
Kinkajous are small, nocturnal animals that live in the rainforests of Central and South America. They are related to raccoons and coatis, and like these animals, they have a long tail and a bushy ringed tail. Kinkajous are also known as honey bears because they love to eat honeycomb and bees.
In addition to honey, kinkajous also eat fruits, leaves, insects, and small mammals.
Do Kinkajous Eat Meat?
Kinkajous are small mammals that are native to the rainforests of Central and South America. They are closely related to raccoons and have a similar appearance, with a long tail, furry body andmask-like face. Kinkajous are nocturnal animals that spend most of their time in trees, where they climb and swing using their long tails for balance.
Kinkajous are omnivores, which means that they eat both plants and animals. Their diet consists mostly of fruit, but they will also eat leaves, insects, small reptiles and even birds. While kinkajous typically avoid eating meat if possible, they will consume it if it is available.
Conclusion
Kinkajous are small, arboreal mammals that are native to the rainforests of Central and South America. They are also known as “honey bears” because of their love for sweet foods. Kinkajous have long, prehensile tails and sharp claws that help them climb trees with ease.
Their diet consists mainly of fruits, but they will also eat flowers, leaves, insects, and small vertebrates.